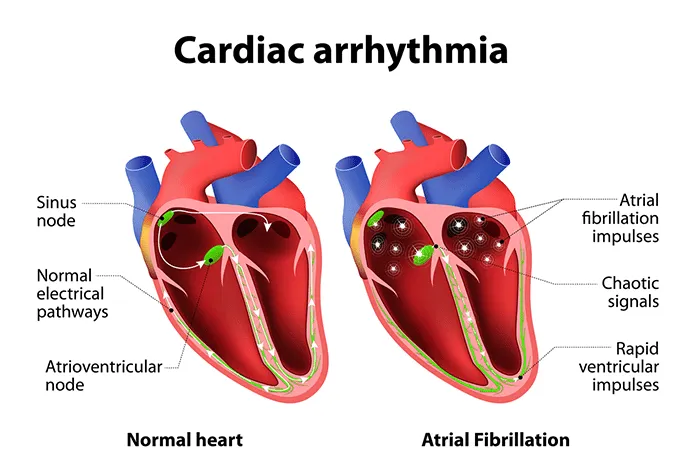
Heart palpitations are a common concern that many individuals experience at some point in their lives. They are characterized by an abnormal awareness of the heartbeat, which may feel like a rapid, pounding, fluttering, or irregular sensation in the chest. While palpitations are often benign, they sometimes indicate an underlying medical condition requiring further investigation. This article helps provide a comprehensive understanding of palpitations, their potential causes, and when to seek medical attention.
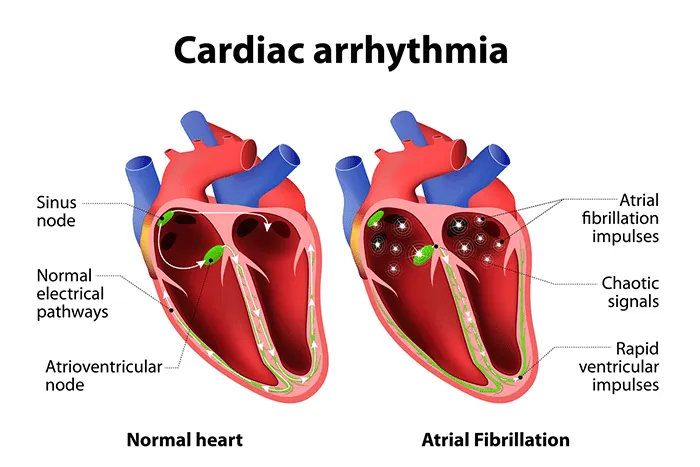
What Are Palpitations?
Palpitations refer to the sensation of being suddenly and acutely aware of your heartbeat. Normally, your heart beats in a steady, rhythmic pattern without much conscious notice. Occasionally, palpitations can cause unusual sensations, including:
- A racing heartbeat (tachycardia)
- A slow heartbeat (bradycardia)
- An irregular heartbeat
- Skipped beats or fluttering in the chest
While irregular heartbeats can occur in healthy individuals with no history of cardiac issues, they may also stem from structural heart problems, arrhythmias, or external triggers. Differentiating between benign and pathological palpitations often requires a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional.
What Are Some Common Causes of Palpitations?
Understanding the causes of palpitations is vital for effective diagnosis and management. While there are numerous contributing factors, they can be broadly classified into physiological, emotional, and pathological causes.
1. Physiological Causes
Certain lifestyle choices and external factors might provoke palpitations in even the healthiest individuals. Common physiological triggers include:
- Caffeine: A stimulant found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and certain medications that can increase heart rate.
- Alcohol: Consuming excessive amounts of alcohol may irritate the heart and lead to palpitations, particularly in individuals sensitive to alcohol.
- Nicotine: Found in cigarettes and vaping devices, nicotine is a stimulant that can exacerbate heart rhythm abnormalities.
- Exercise: Engaging in vigorous physical activity may momentarily lead to a racing heart, which resolves after rest.
- Medications: Some drugs, including decongestants, asthma medications, and thyroid hormone replacements, may induce cardiac irregularities as a side effect.
2. Stress and Emotional Triggers
Palpitations often occur in response to stress, anxiety, or other strong emotions. The body’s “fight or flight” response releases stress hormones like adrenaline, which typically accelerates the heart rate. For individuals prone to anxiety, this creates a feedback loop where increased heart awareness heightens worry, further worsening the palpitations.
3. Medical Conditions
Some underlying medical conditions need careful evaluation as potential causes of palpitations. These include thyroid disorders, heart diseases, electrolyte imbalances, anemia, and in some severe cases, fever or infection. If you have a history of any of these conditions, reach out to your medical professional.
When Should I Seek Medical Attention?
While many episodes of irregular heartbeats are harmless and resolve without intervention, certain red flags warrant immediate medical evaluation. Seek healthcare attention if palpitations are accompanied by:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Dizziness or fainting
- Shortness of breath
- Significant fatigue
To diagnose the cause of palpitations, a clinician may order diagnostic tests, including an ECG (electrocardiogram), blood tests, or imaging studies. These tests help identify arrhythmias, structural abnormalities, or contributing systemic issues.
Lifestyle Changes to Support Heart Health
Adopting certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve heart health and reduce the risk of palpitations. Incorporating regular physical activity, such as walking or yoga, helps to strengthen the heart and promotes better circulation. Additionally, focusing on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall cardiovascular health. Managing stress through relaxation techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises is another effective strategy to maintain a healthy heartbeat. By prioritizing these changes, individuals can take proactive steps toward a stronger and more resilient heart.