High cholesterol is often associated with heart disease and has become a topic of public health focus. Many individuals may not fully understand how cholesterol functions in the body, its link to cardiovascular conditions, or the lifestyle changes that can aid in its management. This article will explain the connection between cholesterol and heart disease while outlining strategies to help manage cholesterol levels effectively.
What is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance present in every cell of the body. It is necessary for producing hormones, vitamin D, and substances that aid in food digestion. The body produces all the cholesterol it needs, but it is also found in certain foods.
There are two primary types of cholesterol:
- Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL): Often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, LDL carries cholesterol to your arteries. Elevated LDL levels can contribute to plaque buildup in blood vessels.
- High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL): Known as “good” cholesterol, HDL assists in removing cholesterol from the bloodstream by transporting it to the liver for processing and excretion.
While cholesterol is involved in various bodily functions, an imbalance—particularly high LDL levels—can pose risks to cardiovascular health.
What Causes High Cholesterol?
Several factors lead to elevated cholesterol levels in the bloodstream. These include dietary choices, lifestyle habits, and genetic predispositions.
- Diet: Foods high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol, such as red meat, fried items, and dairy products, may increase LDL cholesterol levels.
- Lifestyle Habits: Sedentary lifestyles, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption negatively impact cholesterol regulation. Regular physical inactivity, for instance, may lower HDL levels, reducing the body’s capacity to remove excess cholesterol.
- Genetics: Some individuals may have familial hypercholesterolemia—a genetic condition that causes high cholesterol levels regardless of lifestyle choices.
Detecting high cholesterol often requires routine blood tests, as it does not present clear physical symptoms. A lipid panel test measures LDL, HDL, and total cholesterol levels, helping healthcare professionals assess potential cardiovascular risks.
What Role Does Cholesterol Play in Heart Disease?
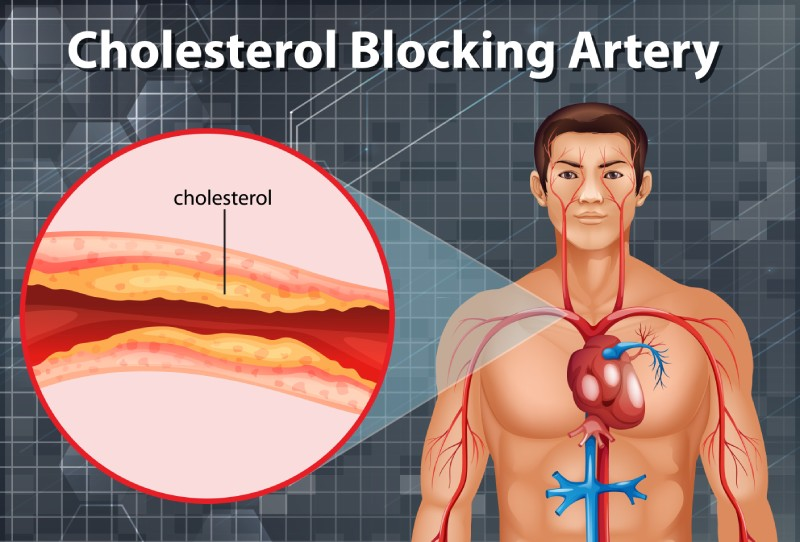
High cholesterol levels, particularly LDL, are closely associated with the development of atherosclerosis. This condition occurs when cholesterol, fat, and other substances accumulate as plaque on the walls of arteries.
Plaque buildup narrows the arteries, restricting blood flow to the heart and other organs. Over time, this restriction can lead to serious cardiovascular conditions, including heart attacks and strokes.
Low levels of HDL cholesterol may further complicate cardiovascular health by reducing the body’s ability to remove excess cholesterol. Maintaining a healthy balance between LDL and HDL is a significant factor in managing heart disease risk.
How Can I Lower My Levels?
Although high cholesterol may pose risks to your health, it is a manageable condition. Adopting specific lifestyle changes and strategies can help regulate cholesterol levels effectively. Some healthy changes include replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats found in foods like nuts, avocados, and oily fish. You can also incorporate fiber-rich foods, such as whole grains, vegetables, and legumes, as they assist in lowering LDL levels.
Physical activity enhances cardiovascular health and helps raise HDL levels. Aim for moderate exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, for at least 30 minutes most days of the week. Maintaining a healthy weight may significantly improve cholesterol profiles. Excess weight tends to elevate LDL cholesterol while reducing HDL cholesterol.
Smoking lowers HDL levels and damages arteries, which can exacerbate plaque formation. Discontinuing smoking and consuming alcohol in moderation can support overall cholesterol management. For some individuals, lifestyle interventions may not be sufficient to address high cholesterol. Healthcare professionals may recommend medications, such as statins, to reduce LDL levels and lower cardiovascular risks.
Steps Toward a Heart-Healthy Life
Cholesterol plays a complex and significant role in cardiovascular health. While the body naturally produces it, elevated LDL cholesterol levels can lead to heart disease over time. By understanding the causes behind high cholesterol and adopting lifestyle changes, heart health is actively supported. For individuals with additional questions or specific concerns about cholesterol management, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended. Detecting cholesterol levels early and implementing strategic changes can contribute to long-term health and well-being.